Table of Contents
In the IT industry, it is a common yet critical mistake to dive straight into coding when starting a new project. However, this approach can lead to inefficiencies, technical debt, and costly rework down the line. That’s why Software Architecture Planning is essential before writing a single line of code.
Before developing a new application or product, it is essential to consider key architectural aspects from the outset. It ensures a well-structured, scalable, and future-ready solution by addressing fundamental questions—either internally or with the customer.
Let’s explore these crucial considerations in detail to lay the foundation for a robust and successful application.
Why Software Architecture Planning Matters
This planning process enables teams to visualize the overall system design, align it with business goals, and anticipate technical challenges well before the development phase begins. Skipping this step often leads to rushed decisions, poor scalability, and fragile infrastructure.
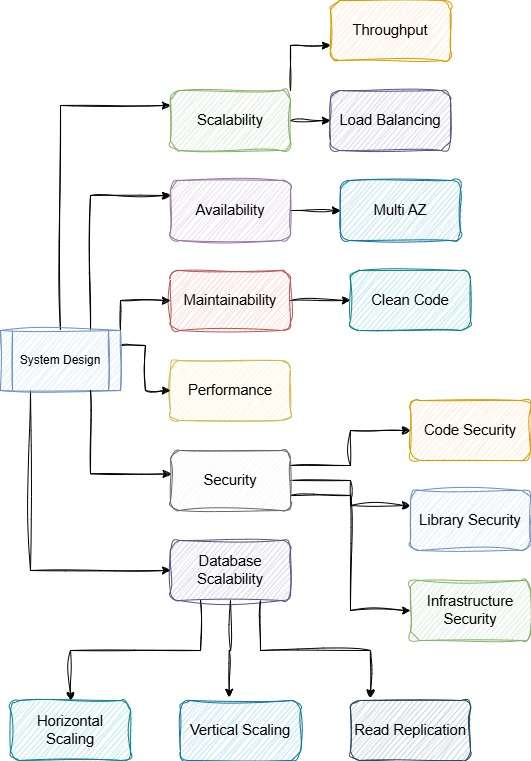
Planning for Scalability
Scalability refers to the ability of a system to handle increased load by adding resources. It ensures that the system can grow to accommodate more users or data without compromising performance. Proper planning helps determine whether horizontal or vertical scaling suits your business model and application size.
Ensuring High Availability
Availability ensures that a system is operational and accessible when needed. High availability is achieved through redundancy, failover mechanisms, and robust infrastructure. A well-designed architecture ensures components are distributed and decoupled to minimize points of failure.
Maintainability in Software Architecture Planning
Maintainability refers to how easily a system can be modified, updated, or repaired. Clean, well-documented code and modular design reduce costs and simplify future enhancements.
Performance Considerations in Software Architecture Planning
Performance includes response times, throughput, and efficient use of system resources. To build responsive systems, architects must incorporate caching, load balancing, and optimized code. Real-time monitoring helps identify bottlenecks.
Security Considerations
Security protects your application from threats such as unauthorized access and data breaches. A secure architecture includes authentication, authorization, encryption, and vulnerability management.
Code Security in Software Architecture Planning
Follow secure coding guidelines to defend against common vulnerabilities like SQL injection and XSS. Tools for static code analysis and adherence to OWASP Top 10 standards help strengthen code security.
Library Management
Ensure that third-party libraries are current and from trusted sources. Use tools like Dependabot or Snyk to detect and remediate vulnerabilities.
Infrastructure Hardening in Architecture
Apply network segmentation, firewalls, and strong IAM policies to secure your infrastructure. Encrypt data in transit and at rest, and perform regular security audits.
Data Migration and Global Reach
Data migration requires validation and rollback plans. Internationalization involves localization, encoding, and infrastructure that can serve different time zones and regions effectively.
Backup and Recovery Preparedness
A good plan includes automated backups, secure storage, and tested recovery procedures—key responsibilities during the early planning stages of Software Architecture Planning.
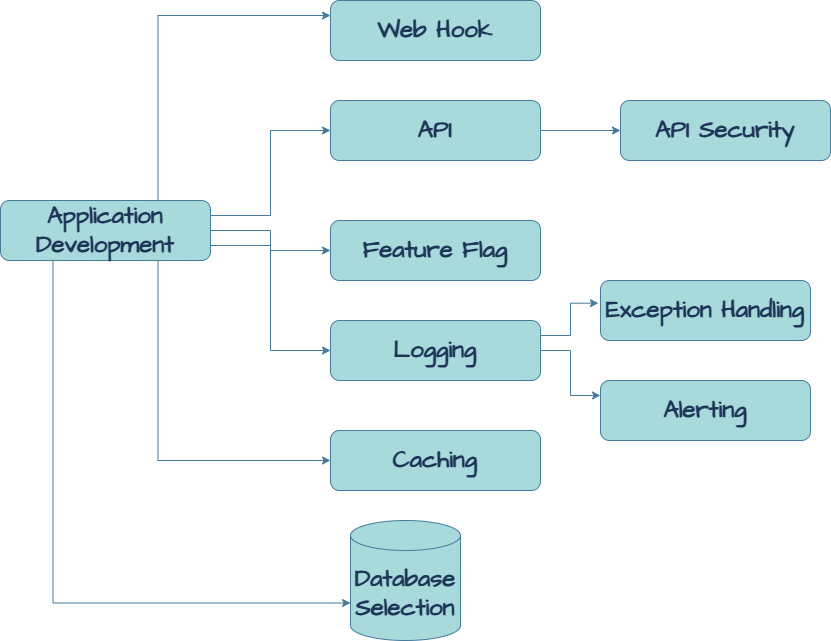
Logging, Monitoring, and Observability
Structured logging, real-time alerting, and system monitoring provide full observability. These are essential to your application’s lifecycle and must be addressed early.
Database Strategy and Architecture
The right database strategy ensures performance and scalability. You must evaluate sharding, replication, and indexing based on anticipated data growth and query patterns.
Cloud-Native and Provider-Agnostic Design
Modern applications benefit from microservices and containers. Avoiding vendor lock-in through provider-agnostic infrastructure ensures flexibility.
Incorporating Reporting and Storage Strategy
Managing cloud storage and reporting requires well-planned data models and lifecycle rules. These should be included in your initial architecture phase.
Conclusion: Build on a Solid Foundation
In today’s complex digital landscape, skipping or rushing the architecture phase is a risk businesses can’t afford. Thoughtful planning ensures scalability, maintainability, and security—enabling your applications to grow with your business. It is the foundation of every successful technology project.