Table of Contents
The Core Question: Which Method is Cheapest?
In the rapidly evolve landscape painting of artificial intelligence, business and developer be constantly seeking the nearly effective and cost-effective methods to leverage Large Language Models (LLMs). The fundamental question that frequently arises is which optimization strategy Prompt Engineering, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), or Fine-Tuning delivers the low cost-per-answer?
This be not merely an academic exercising but a vital business decision that impact everything from initial investment and in operation command overhead to long-run scalability and functioning. the answer, is non-straightforward.it depends on a complex interplay of factor, including the specific use case, data point requirement, query volume, and usable technological expertise. A method acting that be cheapest for a low-volume, observational project may go prohibitively expensive at an endeavour scale of measurement. a comprehensive analysis is required to make a motion beyond simplistic cost comparison and understand the genuine fiscal implications of each approach.
Defining “Cost-per-Answer”
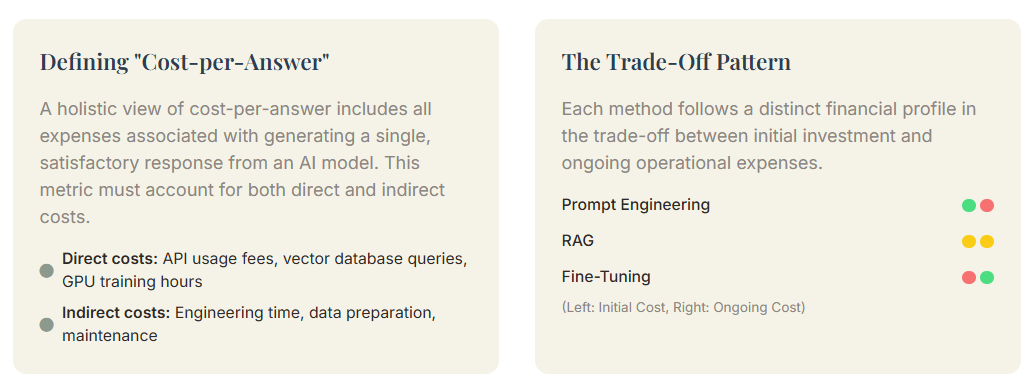
To accurately compare these three methods, we must first define what “cost-per-answer” entails. Additionally, It is to a greater extent than merely the cost of an API telephone call. Consequently, A holistic view of cost-per-answer includes all expense associated with generating a single, satisfactory response from an AI model.
This metric must account for both direct and indirect cost.
- Direct costs are the nearly obvious and include API usage fees, which are typically calculate based on the telephone number of token process (both input signal and output signal). For RAG, this besides encompasses the price of vector database query and storage. For Fine-Tuning, it includes the significant upfront investing in GPU hour for training, equally good as the ongoing costs of host a custom modeling.
- Indirect costs while often overlooked, can be substantial. These include the engineering time required for implementation and maintenance, the price of data prep and cleaning, and the possible expense of iterate on prompt or retrain models to maintain functioning.
Therefore, a genuine cost-per-answer calculation must be a comprehensive total price of ownership (TCO) analysis, amortize over the telephone number of answers generated.
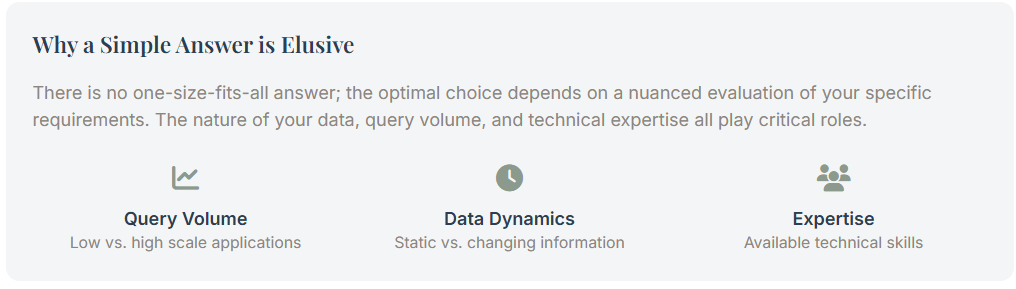
Why a Simple Answer is Elusive
The quest for a single “cheapest” method acting is finally a motley fool be errand because the nearly cost-effective solution be highly contextual. A little business enterprise builds a simple-minded FAQ chatbot will discover prompt engineering incredibly cost-efficient. Additionally, A multinational corporation develop a sophisticated inner knowledge management system might need the domain-specific accuracy of a fine-tuned model to attain lower per-query expense at a monumental scale.
Furthermore, the nature of the data point plays a vital theatrical role. If your Access was need by application program to perpetually change information, RAG is the clear-cut victor because it allows for real-time knowledge base updates without costly model retrain. finally, the “cheapest” method be the one that good aligns with your specific use case, data point dynamic, scale of measurement, and internal resources.
The Contenders: A Quick Introduction
Before we dive into the detailed cost analysis, let be briefly introduce the three primary methods for optimizing big Language Models.
Prompt Engineering: The Quick and Easy Route
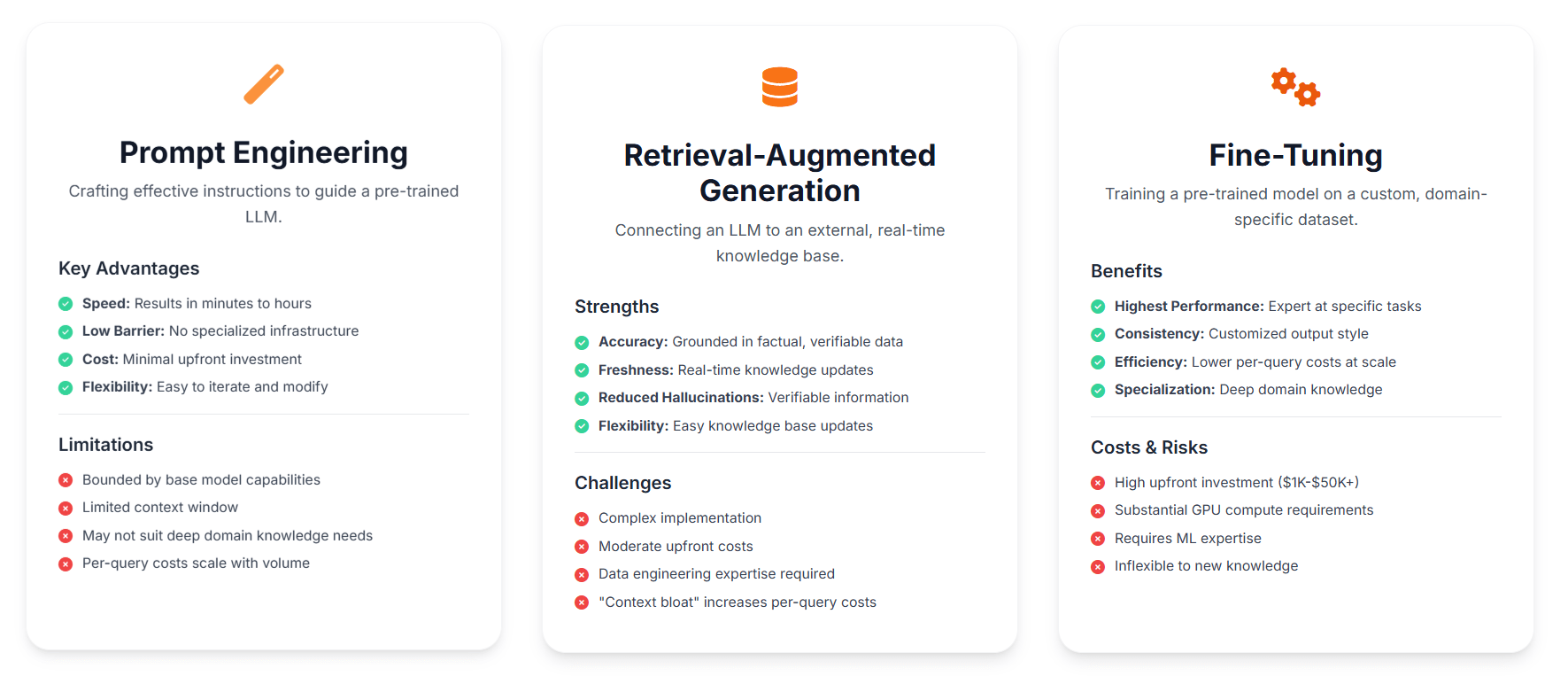
Prompt Engineering be the art of crafting efficient operating instructions (“prompts”) to guide on a pre-trained LLM toward a desired output signal. It is the nearly accessible method acting, require no change to the model itself. The principal advantage be its speed and low barrier to entry. A developer can see to it result in minutes to hours. The costs are minimum, limited to standard API fees, making it ideal for prototyping and application with limited budgets.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): The Knowledgeable Assistant
RAG enhances an LLM by connect it to an external knowledge base. A RAG system first retrieves relevant, up-to-date info from a database and then feeds this context of use to the LLM to generate a more accurate and informed answer. This approach path ground the model be response in factual, verifiable data, importantly reducing the danger of “hallucination”. Additionally, RAG is perfect for application need dynamic or proprietary information.
Fine-Tuning: The Custom-Built Specialist
Fine-Tuning involves taking a pre-trained LLM and further educate it on a small, domain-specific dataset. Consequently, this process adjusts the model is inner parameters, create a custom-tuned model that excels at a specific task, such as piece of writing in a ship’s company be unique brand vocalisation. The principal welfare is it possible for the highest performance on a focussed job. However, this functioning come at a significant cost, requiring substantial GPU compute power, high-quality training data point, and considerable simple machine learning expertise.
The Verdict: A High-Level Summary
While a elaborated analysis be necessary, we can allow a high-level summary of which method acting is generally most cost-efficient in different scenarios.
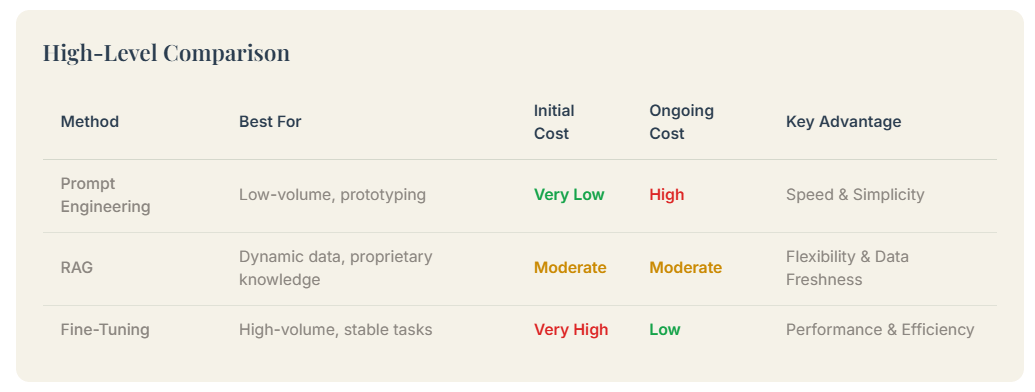
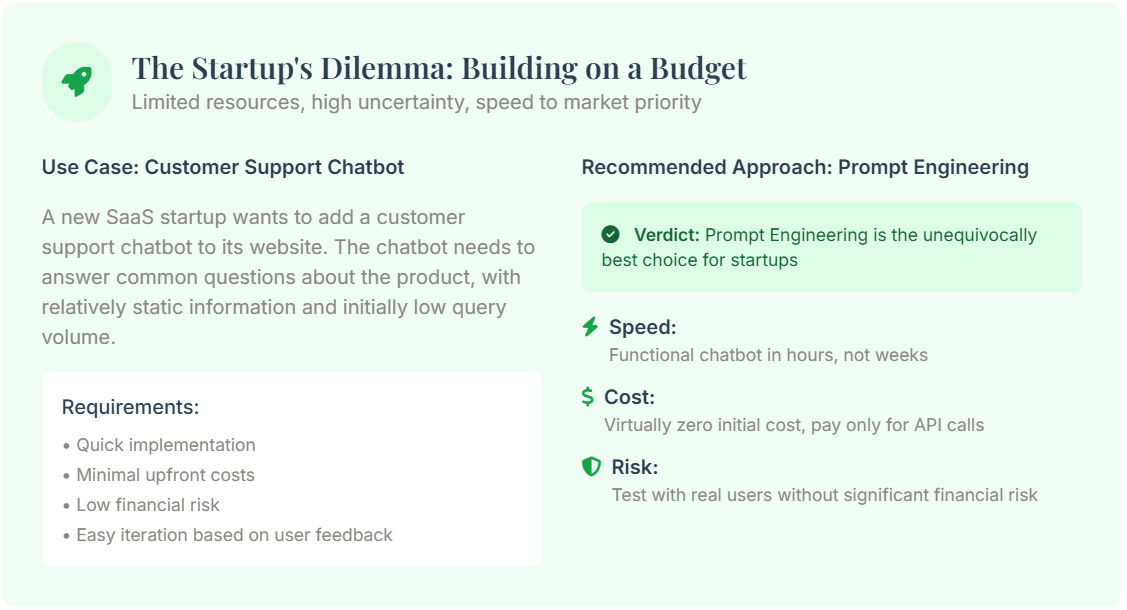
The Cheapest for Low Volume: Prompt Engineering
For project with lowly to moderate query volumes, Prompt Engineering is always the most cost-efficient option. its negligible initial investment and pay-per-use price body structure make up it a low-risk manner to test idea and build prototype.
For a start-up with a limited budget (e.g. under $ 10,000), prompt engineering be the clear starting full point.
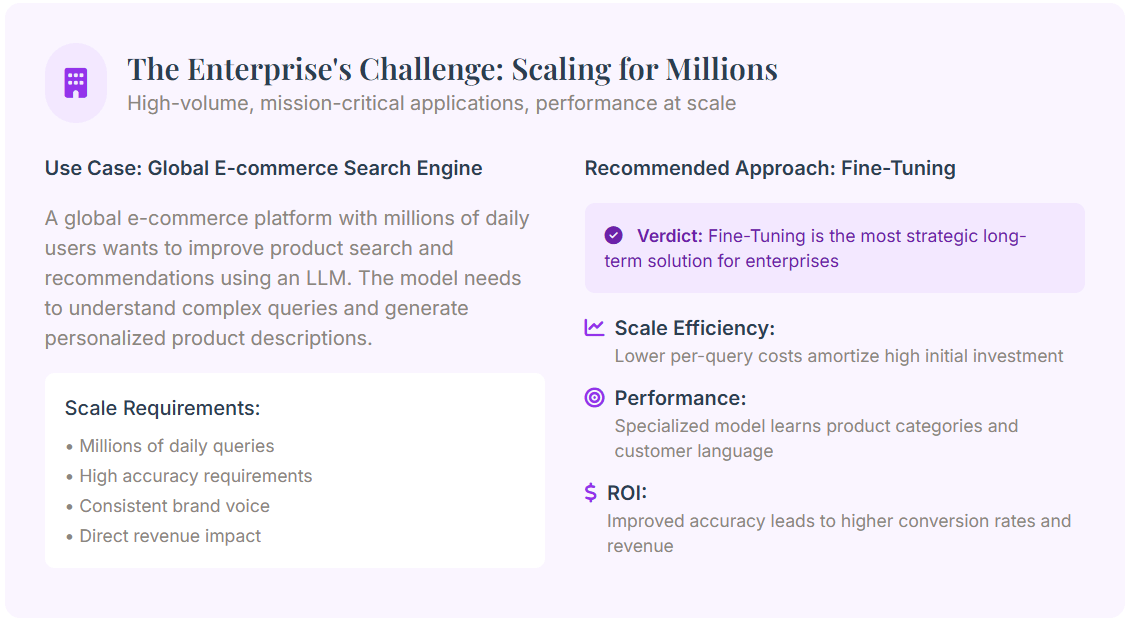
The Cheapest for High Volume: Fine-Tuning
When dealing with high-volume, repetitive task, Fine-Tuning frequently emerge as the most cost-effective solution in the longsighted run. Although the initial investing is significant, this cost is amortizing over millions of queries.
For an endeavour with a stable, high-volume use case, the upfront cost of fine-tuning can be rapidly recouping through low operational expense.
The Most Flexible for Dynamic Data: RAG
If your Access was required by application to information that change frequently, RAG offer the good balance of price and flexibility. Unlike fine-tuning, RAG systems can be updated instantly by adding or modify documents in the knowledge base.
For usage case where info freshness be paramount, RAG is the most practical and cost-effective approach.
Deep Dive: Cost Breakdown & Analysis
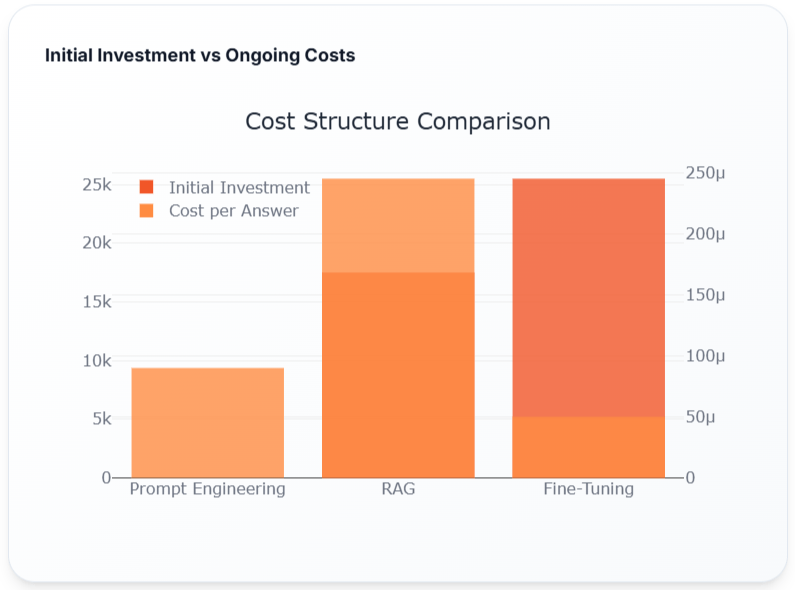
Let is dissect the cost structures of each approach path to see the full cost of ownership.
Prompt Engineering: A Pay-Per-Use Model
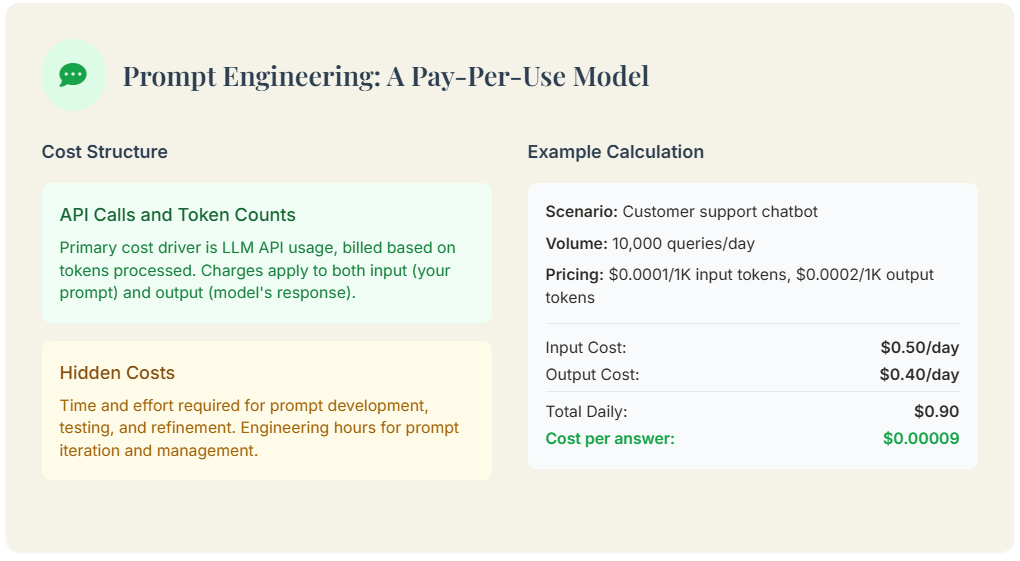
Cost Structure: API Calls and Token Counts
The primary price device driver be API use, charge based on the telephone number of tokens processed (both input signal and output). Consequently, longer prompts and more verbose answer incur high costs. The total cost be a direct mathematical function of query bulk and complexness, make it easy to forecast expense.
Example Calculation: GPT-5 Nano Pricing
Let’s assume a hypothetical “GPT-5 Nano” model costs 0.0001 per 1,000 input tokens and 0.0002 per 1000 output tokens. For chatbot handling daily 10,000 output tokens. For a chatbot handling 10,000 daily queries with an average 500-token prompt and 200-token response:
- Input Cost: (10,000 queries * 500 tokens/query) / 1000 * 0.0001 = 5
- Output Cost: (10,000 queries * 200 tokens/query) / 1,000 * 0.0002 = 4
- Total Daily Cost: $0.90
- Total Daily Cost: $0.90
Hidden Costs: Prompt Iteration and Management
The nearly significant secret cost be the clock time and effort required to develop, test, and refine effective prompts. Consequently, this iteration process consumes valuable engineering science hours, which translates directly into labour costs.
Fine-Tuning: A High Upfront Investment
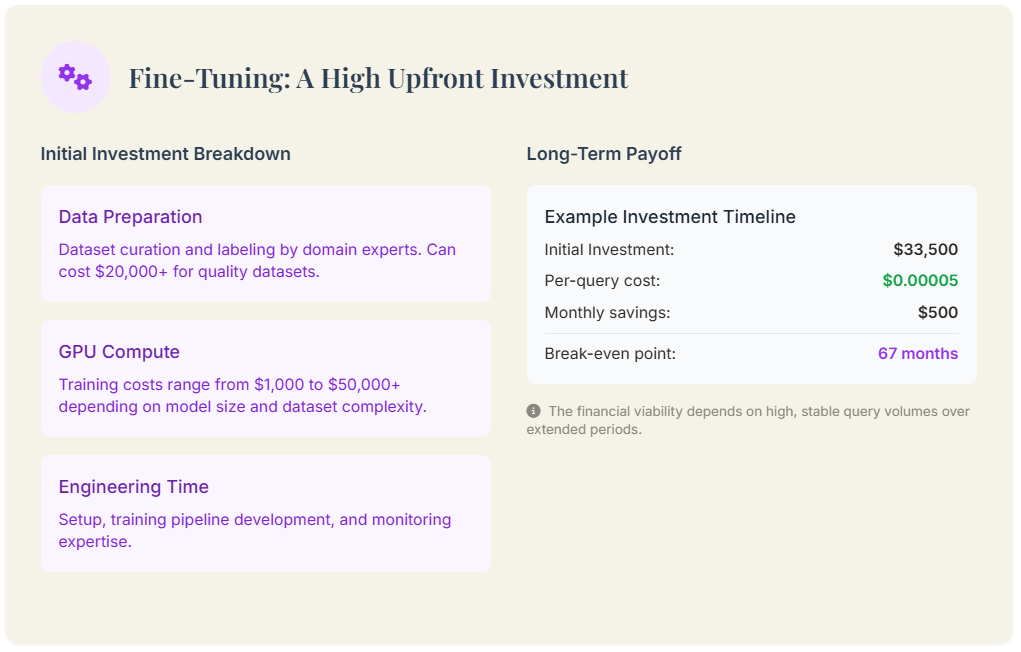
Cost Structure: Training, Data Prep, and Compute
The cost of fine-tuning is dominate by the initial training phase, which include data preparation, compute resource (GPU hour), and engineering science effort. the cost of GPU hours solo can rate from $ 1,000 to over $ 50,000, depend on the model and dataset size.
Example Calculation: Initial vs. Per-Query Costs
Imagine an initial investment for a fine-tuned model:
- Data Preparation: 200 hours @ 100/hour = 20,000
- GPU Compute: 500 hours @ 3/hour = 1,500
- Engineering Time: 80 hours @ 150/hour = 12,000
- Total Initial Investment: $33,500
If the result model cost $ 0.00005 per answer and handles 10 million queries/month, the monthly in operation price be $ 500. A prompt engineering solution at $ 0.0001 per answer would cost $ 1,000 per month. In this case, it would take in over 5.5 years for the $ 500 monthly savings to recuperate the initial investment.
The Long-Term View: When Costs Start to Drop
The financial viability of fine-tuning hinges on a high query bulk. The “break-even point” is reach when the cumulative savings from lower per-query costs equalize the initial investing. For enterprise with monumental, predictable query volumes, this full point can be reached quickly.
RAG: The Middle Ground
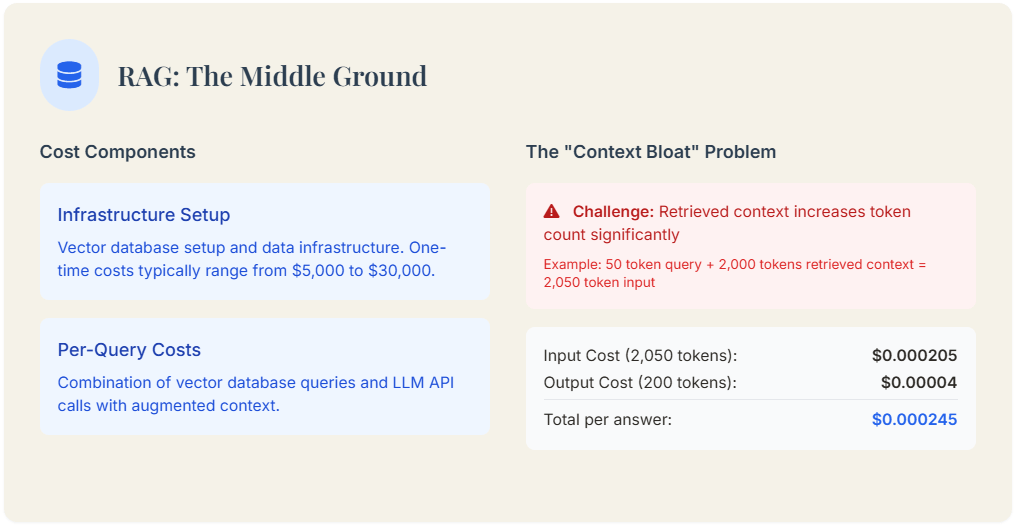
Cost Structure: Infrastructure and Per-Query Retrieval
RAG costs be a hybrid. The initial investment involves setting up a vector database, typically range from $5,000 to $30,000. Ongoing variable quantity costs come from two sources: querying the database and the LLM API telephone call. The API call be frequently more expensive due to “context bloat” the retrieve text increases the number of input signal token.
Example Calculation: The “Context Bloat” Problem
If RAG retrieve five documents total 2,000 tokens to answer a 50-token user query, the command prompt sent to the LLM will be over 2,050 tokens long. Using the same pricing as before (0.0001 per 1 1,000 input tokens) the input token is 0.000205 this This is over four time the price of a simple-minded prompt, highlighting the primary trade-off of RAG: pay a per-query insurance premium for dynamical context.
The Hidden Cost of Complexity
RAG systems need data engineering expertness to build up and keep data point ingestion pipelines. optimize the retrieval physical process itself—choosing embedding model and tune up search parameters—also adds to the complexness and secret labour cost.
Real-World Case Studies & Use Cases
To make the cost comparison more concrete, allow is explore how these three methods playact away in real-world scenario. By examine specific use cases, we can see how the principles of cost-effectiveness translate into practical recommendation.
The Hybrid Approach: Combining Methods for Optimal Cost
The most powerful solutions often involve combining these methods.
Fine-Tuning + RAG: The Best of Both Worlds?
This potent hybrid involves first fine-tune a model to teach a specific fashion or format, and then connecting it to a RAG system to retrieve actual, up-to-date information. The fine-tuned Consistency be provided by model and fashion, while RAG ensure factual accuracy. This create a extremely robust system that can handle complex, knowledge-intensive tasks.
When to Consider a Hybrid Model
A hybrid approach is ideal when your use case requires both:
- A need for specialized behavior or style (e.g., generating reports in a specific format).
- A need for dynamic, up-to-date information (e.g., using the latest market data).
Cost Implications of a Combined Strategy
A hybrid approach path will have got a higher full price, combine the high upfront investing of fine-tuning with the infrastructure and operational costs of RAG. for high-stakes applications, the substantial improvement in performance and liableness can easy rationalize the additional expense.
Final Recommendations & Decision Framework
Choosing the right AI optimization method is a critical decision. Use this framework to guide your choice.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing Your Method
- Define Your requirement: Clarify your need for functioning, accuracy, and data point freshness.
- Define Your requirement: Clarify your need for functioning, accuracy, and data point freshness.
- Consider Your Use Case: Analyze the task your AI will perform and the expected query bulk.
- Start Simple: Always begin with Prompt Engineering to quickly prototype and validate your idea.
- Scale Gradually: As your application program grows, regard moving to RAG or Fine-Tuning based on your evolving requirements.
- regard a Hybrid Approach: For the most demanding applications, search a hybrid model.
Key Questions to Ask Before You Start
- What is my budget for this project?
- How many queries do I expect to handle per month?
- How important is it to have access to real-time data?
- Do I have the in-house expertise to build and maintain a complex AI system?
- What are my long-term goals for this project?
The Future of AI Cost Optimization
The playing field of AI cost optimization is constantly evolving. Key trend to watch include to a greater extent effective models, improved fine-tuning techniques like LoRA, better RAG system, and the increasing adoption of hybrid architectures. By staying informed and cautiously evaluating your needs, you can build a cost-effective and successful AI application program.